Table of Contents
- Plasma Cutting Process
- Understanding Plasma Process – Advantages & Disadvantages
- Gas Cutting or Oxy fuel Cutting Process
- Gas Cutting or Oxy-fuel cutting Advantages
- Gas Cutting or Oxy-fuel cutting Disadvantages
- Key Benefits of Hypertherm Powermax SYNC
- Summary
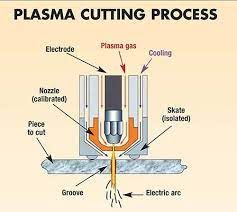
Plasma Cutting Process:
Electricity and pressurized gas combine to form a plasma arc of ionized gas. This super-hot
plasma instantly melts metal. The gas shapes the arc and blows molten metal away, leaving a smooth cut edge.
Plasma cutting systems consists of:-
- Plasma Cutting power source
- Compressed air to enable cutting
Understanding Plasma Process – Advantages & Disadvantages
To understand the unique advantages of Plasma Cutting process we need to compare to the conventional Oxy-Acetylene cutting process used in Industry.
Plasma cutting using plasma cutting power source with compressed air is used for cutting all electrically conductive material both ferrous and non-ferrous metals, while in Oxy-fuel cutting with a Gas Cutting torch, oxygen and acetylene gas is used for cutting steel/ferrous material therein lies the major difference.
Now let us understand in both Plasma cutting process & Oxy-Fuel cutting process in detail.
Plasma Cutting: Capabilities & Advantages
- Cut and gouge any electrically conductive metal – MS, SS, AL, alloys, others
- Plasma Cutting can cut rusted plates , paint surface & even fatigued stacked metal
- Cutting done with compressed air. No use of costly gases like Acetylene or Oxygen
- Can do clean cut up to 50m thick, without pre-heating faster than any process.
- Easy to use with simple plug and play method
- Easy to automate
- Small heat-affected zone
- Can be used for cutting wire mesh and even complex filter systems
- Plasma Cutting machines are available with portable capability
- Portable Plasma system with inbuilt compressor for all site applications
- Faster process and easy to teach & train welders
- Very safe process for the welder and user
- Some plasma cutting equipment like Hypertherm has capability of operating on input voltage from 200 V to 600 V. This means the same machine can be used with single phase as well as three phase circuitry.
Plasma Cutting: Disadvantages
- Can’t heat metal for bending
- Initial Cost of these systems is very high even though it offers good return on investment.
- Can’t efficiently cut much thicker than 75mm MS
- Requires Electrical Energy or Electricity for cutting process.
- Requires compressed air for cutting
- Slightly complex settings for the welder in comparison to oxy-fuel cutting
- Metal warping and heat affected zone
Gas Cutting or Oxy fuel Cutting Process:
Oxy-fuel cutting torch heats a ferrous metal to ignition temperature (or) plastic state with an oxy-acetylene gas induced flame. So with a press of lever we introduce the cutting oxygen this further combusts and reacts with the metal to create iron oxide (slag) that blows and cut the metal away.
In this process a Gas Cutting system, Oxygen gas cylinders and Acetylene cylinders are primarily used for the cutting purpose
The hazards caused by this process are
- Chances of fire accident as welder handles heat, sparks, molten metal, or even direct contact with the flame
- Process becomes very dangerous while cutting tanks or drums which contain Flammable materials
- Fire/explosion caused by gas leaks, backfires and flashbacks
- Fumes created during flame cutting
- Fire/burns resulting from misuse of oxygen
- Burn Injuries due to accidental contact with the hot flame or hot metal
- Injuries caused during transportation and handling of heavy gas cylinders

- Can effectively cut steel only and effective when cutting over 50mm.
- Use anywhere cylinders are available.
- Relatively low initial acquisition cost
- Heat metal for bending.
Gas Cutting or Oxy-fuel cutting Disadvantages:
- Cuts only mild steel.
- Metal must be pre-heated to pierce.
- Hard to cut heavily painted rusted or stacked metal.
- Speed of cutting lower in comparison to plasma cutting
- Hand cutting requires skill – stand off
- Must use flammable gasses.
- Metal warping and heat affected zone
Hypertherm’s Powermax SYNC the latest generation of Plasma Cutting machines are loaded with features & benefits for customers.
Key Benefits of Hypertherm Powermax SYNC

- Easy-to-identify the single-piece cartridge consumables as they are color-coded. This eliminates confusion on identifying parts and simplify consumable inventory.
- New SmartSYNC® torches with the Hypertherm cartridge synchronises the correct amperage and operating modes eliminating setup errors
- Highly versatile can do a wide range of jobs with easily interchangeable torches and application-specific cartridge consumables.
- Life of Consumables can be monitored as end-of-life detection signal lets you know the time to change your cartridge
Productivity gains
- Very simple operation ensures minimum downtime, troubleshooting and training time.
- Advanced cartridge design increases life to twice for hand cutting, and improved quality of cutting and life in mechanized setups compared to conventional consumables.
- Each cartridge has been custom designed to optimize the cutting or gouging performance
Innovative smart system
- End-of-life detection signal gives the operator right time to change the cartridge
- Advanced torch communication for automated process setup
- Time-saving controls directly on the torch allow you to adjust amperage and change the consumable without returning to the power supply
- Live access to cartridge performance, enables tracking and analysing usage patterns
- Cartridge reader app pairs with Powermax SYNC smartphone app to record & analyse performance data.
Industry-leading reliability
- Engineered for rugged, industrial environments
- SpringStart™ technology gives consistent results in repetitive applications.
Summary:
- Oxy-fuel and plasma cutting are all well-established cutting processes used for Cutting steel. Each has its merits and demerits, but are used as per specific Business needs.
- Oxy-fuel has the lowest investment and operating cost, though the costs of cutting per part in the end are higher due to slow cutting speeds and lower cut quality, which often requires more Secondary operations meaning more expenditure on labour. Oxy-fuel is predominantly used for cutting only thick carbon steel when cut quality is not the Criteria.
- Plasma provides a ideal balance in terms of capital cost, cut quality, productivity and operating costs. It has significant thickness cutting range and can variety of ferrous and non-ferrous, so it’s very versatile process with higher cutting speeds.
Hence with safety and personal protection of the user becoming vitally important, industry is moving more and more towards Plasma cutting for most of the hand cutting applications.
Ador Fontech Limited, the name synonymous with total solutions for any Maintenance & Repair solutions, recommends Hypertherm plasma cutting with Duramax Torch and consumables as a robust plasma cutting solution to all our customers for all Cutting and Gauging applications in their premises.